Nigeria Signs a Bill to Enable all 36 States to Generate, Transmit and Distribute Power
Nigeria States to Generate, Transmit and Distribute Power
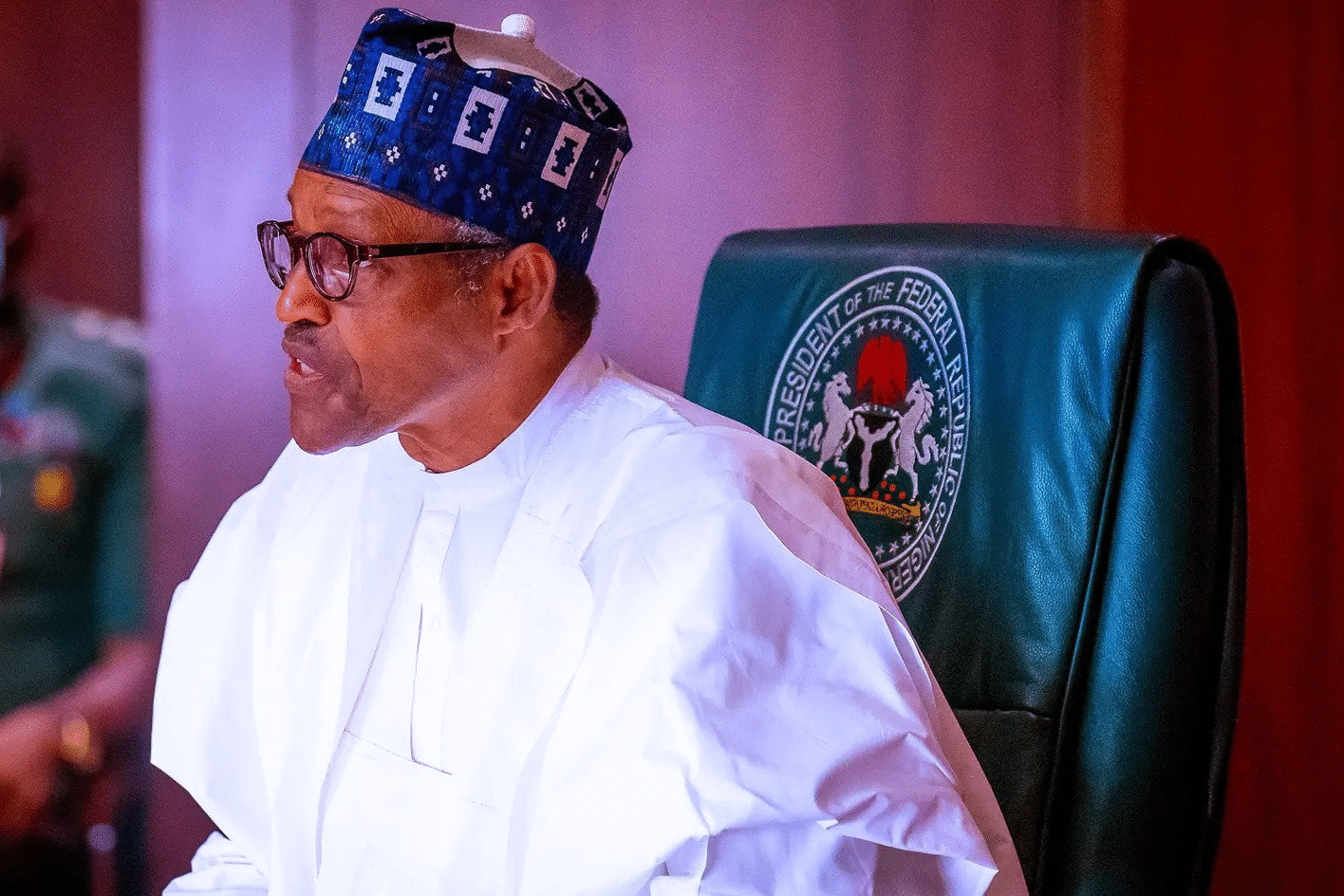
President Buhari has signed an amended constitution that gives Nigerian states greater power to generate, transmit and distribute their own electricity.
This development is aimed at addressing the country’s lingering power challenges by promoting competition, driving efficiency, and ultimately improving access to electricity across Nigeria.
The amendment will enable state governments to partner with private companies to generate power, use the national grid for transmission, and sell electricity to customers within their territories.
Australian Researchers Surpassed 30% Efficiency with Tandem Perovskite-Silicon Solar Cell
Nigeria’s Presidential Media Spokesperson Tolu Ogunlesi wrote on Twitter:
JUST IN: President @MBuhari has signed. Constitution Amendment Bills into Law.
By this signing. State Houses of Assembly & Judiciaries now have constitutionally-guaranteed financial independence, while Railways have moved from Exclusive Legislative List to the Concurrent List.
Another landmark change: By virtue of the Presidential Assent, Nigerian States can NOW generate, transmit and distribute electricity in areas covered by the national grid. Wasn’t allowed pre-amendment. This is genuine, realistic Restructuring – through the Constitution.
Nigeria’s Presidential Media Spokesperson Tolu Ogunlesi
What Does This Mean To Nigeria: States to Generate, Transmit and Distribute Power
This move is expected to boost electricity supply across the country, as state governments can now take responsibility for generating power to meet the needs of their citizens.
WE CARE SOLAR – 1000+ Solar Suitcase Installations Milestone Reached in Zimbabwe
This development marks a significant step towards resolving Nigeria’s longstanding electricity challenges, as it provides an opportunity for private sector investment in the power sector.
This will, in turn, create jobs, boost economic growth, and raise living standards across Nigeria.
The new policy will also foster innovation and encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources, which will help to address environmental concerns and promote sustainable development in the country.
10 Global Trends in the Solar Sector
Furthermore, this policy is a great move to drive investment and innovation from the private sector. Let’s wait and see the outcome. Perhaps to check the results and progress of this policy after a few years.
Nigeria’s Energy Sector Challenges
Perhaps this move of Nigeria States to generate, transmit and distribute power is meant to curb the power challenges in this African country.
Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa and has a rapidly growing economy. However, the country’s energy sector faces numerous challenges that hinder its ability to meet the growing demand for electricity and fuel.
Insufficient power generation: Nigeria’s power generation capacity is insufficient to meet the country’s demand for electricity. The country’s power generation capacity is only about 12,000 MW, while the demand for electricity is estimated to be around 30,000 MW.
Poor infrastructure: Nigeria’s energy infrastructure is outdated and inadequate, with many power plants and transmission lines in need of repair and modernization. This results in frequent power outages and disruptions, which impact businesses and households.
Zimbabwe Announces Solar Incentives for 1GW IPP Projects
Low access to electricity: Only about 45% of Nigerians have access to electricity, with many rural areas lacking access to reliable and affordable electricity. This limits economic development and makes it difficult for households to access essential services such as healthcare and education.
Dependence on fossil fuels: Nigeria’s energy sector is heavily dependent on fossil fuels, particularly oil and gas. This dependence makes the country vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices and limits the development of renewables and other sustainable energy sources.
Corruption and mismanagement: Corruption and mismanagement are significant challenges in Nigeria’s energy sector, with reports of embezzlement, bribery, and other forms of corruption. This hinders the development of the sector and undermines public trust in the government’s ability to manage the country’s energy resources.
Conclusion
This policy of Nigeria States to generate, transmit and distribute power will promote competition and private sector investment in the Nigerian power sector, increase electricity supply, and ultimately improve the quality of life for Nigerians.
It is a step in the right direction towards addressing Nigeria’s energy challenges and promoting economic growth and development.
Nigeria’s energy sector faces numerous challenges that require urgent attention and action. Addressing these challenges will require significant investment in infrastructure, modernization of the energy sector, and a shift towards sustainable and renewable energy sources.
It will also require a commitment to transparency, accountability, and good governance to ensure that the country’s energy resources are managed in the best interests of all Nigerians.
FOLLOW US ON SOCIAL MEDIA
Follow us on LINKEDIN, FACEBOOK, TELEGRAM GROUP and WHATSAPP.
*** ALSO CHECK: VITALITE – Electrifying Zambian rural and peri-urban households through solar
HOW TO SIZE A SOLAR SYSTEM – 5 clear steps anyone can follow
HOW TO START A SOLAR COMPANY – do these 6 things and make money through solar
How to Identify Fake Solar Products